As Korea’s domestic and foreign situation has deteriorated, the so-called ‘April crisis,’ meaning that all bad situations will be exacerbated climatically, has emerged. There are _ve main issues that have led to the ‘April crisis,’ and the most prominent factor is the announcement of currency manipulators, which the United States (US) will select, based on their next foreign exchange report that will be published on April 15th. Therefore, the Sungkyun Times (SKT) will now introduce the concept of currency manipulation, sanctions imposed on currency manipulators and will explore the stances of countries related to this, as well as its effects on Korea.
Concept of Currency Manipulators
A Currency manipulator is a country whose government or central bank arti_cially intervenes in the foreign exchange market to manipulate the exchange rates between foreign currencies and domestic currencies in order to increase its exports and to secure the competitiveness of their products. Since 1988, the US Department of the Treasury has created a currency exchange report every April and October and submits it to Congress. Then, the president designates which governments or central banks it believes to be currency manipulators and adds them to a monitoring list. Countries that need close monitoring depend on whether the government intervenes in foreign exchange rates, in order to make their conditions of trade advantageous over the US. The US law stipulates that any country meeting three statutory criteria can be designated as a currency manipulator. Firstly, their trade surplus with the US must exceed $20 billion. Secondly, the ratio of the current account surplus to the gross domestic product (GDP) should exceed 3%. The current account is the total result of trade of products and services, and if the money earned is more than paid, then it is referred to as “surplus.” Thirdly, the authorities’ intervention in the net purchase of dollars should amount to over 2% of the GDP. If a country satisfies all of these three conditions, then they can be designated as a currency manipulator, and if it satis_es two of them, they will be placed on the monitoring list. Additionally, according to the Trade Facilitation and Trade Enforcement Act of 2015, a country listed on the monitoring list should be on it at least two times, before they are designated a currency manipulator.
Sanctions Imposed on Currency Manipulators
When a country is designated as a currency manipulator, the US Treasury Secretary conducts a bilateral dialogue with that country. During the dialogue, they take a look at the reasons for the depreciation of the exchange rate and the huge surplus of trade with the US. Moreover, the Secretary unveils the economic damages that the US has received, and then requests the country in question to revise their exchange rate policy. If there is no change in attitude over the next year, the US government can impose one or more sanctions.
1. Prohibition of Funding Through the Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC)
OPIC is an agency created in January 1971 to promote US private capital and technology investments in newly industrial countries. In fact, many US companies are supported by OPIC. According to research by NH Investment and Security, in 2015, a total amount of $14.2 billion new investments were made by OPIC in 38 newly industrialized countries. Without OPIC’s support, each company is expected to bear all of the risk made from the local investment. Therefore, if the funding from OPIC is prohibited, the investment from US companies is likely to decrease.
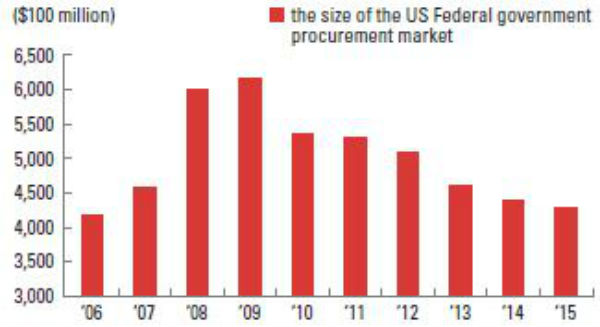
2. Prohibition of Entering into the US Procurement Market for Products and Services
Procurement means delivering products. For example, if Korea supplies products to the US, then the US becomes a procurement market for Korea. Data from NH Investment and Security in 2015 also shows that the US is one of the biggest markets in the world, with a total value reaching $437 billion. Thus, if entry to the US procurement market is forbidden, it would become difficult for foreign companies to sell products into the US market, which could cause huge economic trouble for the country in question.
3. Pressure on the Exchange Rate Though the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
The original role of the IMF is to stabilize foreign exchange rates, remove various foreign exchange restrictions, and give funds to countries in need. Additionally, since the US has 17% of the total stake, which is the largest among those of all other countries, the influence the US has on the decisions made by the IMF is enormous. Therefore, the US can also request the monitoring of exchange rate policies and their economic conditions through American IMF directors. In fact, in April 2016, the US Department of the Treasury demanded the IMF to act more aggressively to major global economic problems, including foreign exchange volatility and current account imbalances. Moreover, on February 21st, Steven Mnuchin, the Secretary of the US Department of the Treasury, urged the IMF to openly and equitably analyze the exchange rate policies of IMF member countries. It is the same as the Donald Trump administration requiring the IMF to determine if there is a country that can be designated as a currency manipulator and provide the evidence required for designation. Thus, just like putting pressure on an international organization, a designated country can be restricted from intervening in the exchange market.
4. Linkage Implementation with Trade Agreements
The _nal sanction that the US can introduce is to re_ect the efforts of the country to reduce its trade surplus and correct the currency rate, when or if the US enters into a new trade agreement with that country. In addition to these sanctions, the difficulties to the economy all around the country are likely to increase if the value of the currency of the country increases during any sanctions. Moreover, the international stock market will almost certainly _uctuate depending on which country is designated as a currency manipulator.
Positions of Many Related Countries
The United States
The US is showing a strong will to designate currency manipulators. Donald Trump, the US President, insisted that he will designate major countries as currency manipulators after his election, and con_rmed that he will do so on the 100th day of his inauguration. In particular, the US is highly likely to designate China as a currency manipulator because the US will be looking to keep China in check. Additionally, the US can change the law of three statutory criteria if they need to. In October 2016, China met only one criteria, but the US designated China as a country that should be monitored by revising the Trade Facilitation and Trade Enforcement Act, saying that a country on the monitoring list should be on there two times at least. If the US changes the law again to designate China as a currency manipulator, then there would be a high possibility that Korea, Taiwan, and Japan will also be included in the new baseline and be designated as currency manipulators.

China
The US is likely to designate China as a currency manipulator; however, if they really do so then China is expected to take a variety of measures in response. According to research by NH Investment and Security Research Division data in November 2015, China has the second largest number of US bonds in the world, of which the value is estimated at $1,493 trillion, 18% of US’s total number of bonds. If China sells them as a response to any measures that the US takes, then the interest rate of government bonds will rise, weakening the move of the US economic recovery. Additionally, China can carry out trade retaliations against the US. The government can impose retaliatory tariffs on US imported goods and make many limitations on importing products.
Other Countries That Are Accused of Currency Manipulation
In these cases, the head of power in many countries are strongly opposed to it. Shinzo Abe, the Prime Minister of Japan, argued that criticism towards currency manipulation is not right and he would discuss it in a summit meeting with Donald Trump on February 10th. Moreover, Suga Yoshihide, the chief cabinet secretary of Japan stated that Japan’s ‘easy money’ policy, which led to the Yen depreciation, is to seek price stabilization, not to lead a depreciation of the Yen. During the summit meeting held on February 10th, however, conversations about sensitive issues like currency rate were not discussed. Moreover, in the interview right after the summit meeting with Abe, Trump strongly argued that he has been disgruntled by the countries that have devalued currencies for the longest periods of time, and he will put the US, Japan and China at the forefront of fair competition. Angela Merkel, the chancellor of Germany is also strongly disagreeing with the statements of Donald Trump. Trump said that Germany is devaluing the Euro and exploiting other countries. While on the other hand, Merkel stated that Germany does not have any direct impact on the Euro and is always supporting the independence of the European Central Bank.
Situation of Korea
In the Past
Korea was designated as a currency manipulator three times in succession, between October 1988 and March 1990. At that time, Korea’s amount of trade surplus against the US was continually increasing, so the US Department of the Treasury was dissatisfied with Korea’s currency market. In order to lift the designation of being a currency manipulator, Korea changed its exchange rate system. In 1988, Korea was operating a multi-currency “basket system”, which related to the currency of many other major countries and selected the exchange rate. This system changed to the Market Average Exchange Rate System, which selects the exchange rate according to the supply and demand of the market. As a result, in 1990, the US Department of the Treasury announced that a change in the exchange rate system had lowered the evidence of currency manipulator and canceled the designation.
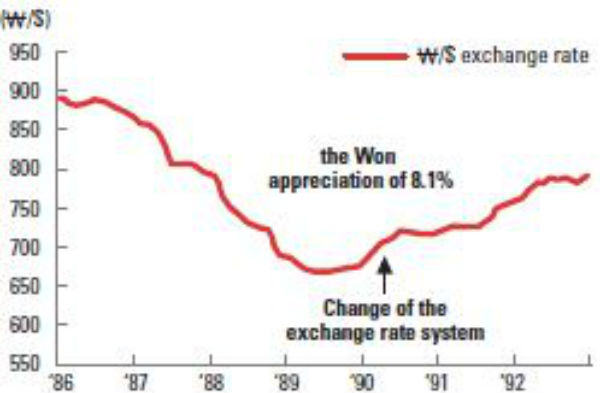
These two years of designation had a very negative impact on the Korean economy. Comparing 1987 and 1989, which were right before the designation and right after the designation, the value of the won against the dollar rose by 20%, and real GDP fell to 5.4% in just two years.
In the Present
Korea was on the monitoring list in both April and October of 2016 along with China, Japan, and Germany. Currently, Korea satis_es criteria one and two. Data from 2016 shows that Korea’s trade surplus with the US was $30.2 billion, current account surplus to GDP was 7.9%, and dollar purchases to GDP was -1.8%. Therefore, although it is likely to be designated as a country that should be on the monitoring list, the possibility of the Trump administration changing the criteria rule and designating Korea as a currency manipulator is not ignorable.
In the Future
If Korea is designated as a currency manipulator and receives sanctions from the US, then the Korean economy is expected to fall into serious trouble since Korea relies heavily on exports. Additionally, if China is designated as a currency manipulator, the currency of a newly industrialized country will be pushed into a decline, as the trade conflict between the G2 intensifies. In particular, in the case of Korea, which is sensitively affected by China, the value of assets such as stocks and bonds are likely to decline and foreign funds will also be withdrawn. All of these impacts will lead to a rise in won-dollar exchange rates. The dissatisfaction that Trump has towards Korea is that Korea does not allow the won-dollar exchange rate to be _exible based on market principles, but intervenes in the market in order to control the exchange rate. From the standpoint of the US, Korea is a country that keeps high stability of its exchange rate. Korea is, however, unable to let the exchange rate move fully based on market logic because of the stabilization of the Korea domestic _nancial market. In the short term, to prevent designation as a currency manipulator, the Korean government may suggest that trade surplus is the result of other factors, not the depreciation of the exchange rate. The logical result of analysis which can objectively show that other factors, such as technological competitiveness differences, low oil prices, which are not related to exchange rates, but produce trade surplus, is needed. Moreover, in the long run, Korea must also consider ways in which to increase the transparency of foreign exchange market intervention.
As time goes by, and April is drawing near, many countries will be starting to worry about whether they will be designated as currency manipulators, and it is the same with Korea, too. Of course, nobody knows who will be designated, and what exact impact the designation will have on the international exchange market. In order to decrease the negative impact from designation, however, from now on, the Korean government should keep a closer look out for the movements of many major countries, and try to minimize the negative impact that currency manipulation designation would have on the Korean economy.
