
At the European Union (EU) summit held on March 21st, 2019, the EU and the United Kingdom (UK) agreed to delay Brexit until April 12th, and if Brexit agreement is approved in the House of Commons in the UK, Brexit will be delayed until May 22nd . Brexit is the shorthand way of expressing the UK's withdrawal from the EU, combining the words Britain and exit. As the problems that need to be 'solved before Brexit are continuing, a “no-deal” Brexit, which refers to the UK’s withdrawal from the EU without any negotiations, is most likely to happen. A no-deal Brexit could have huge side effects inside and outside the UK and it is widely regarded as being “the worst choice”. Accordingly, the Sungkyun Times (SKT) is going to look over the background information of the no-deal Brexit, the problems regarding a Brexit deal, and the potential impacts.
Background Information on No-deal Brexit
-A Referendum and Negotiation with the EU
The UK has been skeptical about remaining a member of the EU for a long time for a number of complex reasons. The UK became pessimistic about reinforcing its political union with the EU. Also, the UK has little clout and benefits from the EU in comparison to its increasing contributions made to the group. Due to a number of these reasons, a referendum was held in the UK on June 23rd, 2016, to decide whether the UK should leave the EU or remain. After the “leave” side won by 51.9% to 48.1%, the UK started a procedure for Brexit over a two-year negotiation period, which started from March 29th, 2017. After an early general election in the UK in June, the UK and the EU started to negotiate face to face for the first time on November 14th, 2018 and began an internal approval process respectively.
-The After-effects of Negotiation in the EU
The European Council recognized the agreement bill on November 25th, 2018. The Brexit agreement consists of the withdrawal agreement and the declaration on future relations. The former is a legally binding document which is mainly about measures to settle the relationship between the UK and the EU. It has four major contents: a settlement on the financial obligations of the UK, a guarantee on the vested rights of the UK citizens living in other EU countries, an issue on the border between Ireland and Northern Ireland, and an application of a transition period after the withdrawal of the UK until launching future relations between the UK and the EU, which is from March 30th, 2019 to December 31st, 2020. The withdrawal agreement focuses on building strategies to minimize disorder and damage. The declaration on future relations includes the conception of their long-term future relationships. European Council will pass a proposal on ratification. After that, the rest of the procedure is the final approval of the EU summit. As the Parliament of the UK finishes ratifying the deal, the European Parliament and the EU summit will go through the approval process. The withdrawal agreement would take effect based on a vote in the House of Commons in the UK.
-The After-effects of Negotiation in the UK
Whether this agreement is approved or denied in the House of Commons is uncertain because of political divisions. In fact, the vote on approving the Brexit agreement planned on December 11th, 2018 was postponed by the prime minister of the UK, Theresa May, as getting the votes for the majority was effectively impossible. Then, a vote took place on January 15th, 2019, and the agreement was rejected by a margin of 230 votes, an overwhelming majority (Agreement 202votes, Disagreement 432-votes). The possibility of passing the agreement and leaving the EU in an orderly way is decreasing as conflicts in the political world in the UK get more intense. The Conservative Party, which is the ruling party, is struggling with internal conflicts, and the opposition party keeps opposing the agreement. The agreement on Brexit and the vote to decide to implement a no-deal Brexit were rejected in the House of Commons on March 12th and March 13th respectively. On March 21st, Theresa May officially requested to delay Brexit until June 30th at the EU summit in Brussels, but her request was denied since the EU was concerned about the next selection of the European Council that is scheduled in May. Then, the EU and the UK agreed to postpone Brexit until April 12th or until May 22nd if Brexit agreement is approved in the House of Commons. On March 23rd, more than one million people gathered for a march to support a second referendum on Brexit in central London, under the slogan, “Put It to the People”, which was one of the largest rallies the UK has seen for some time. Also, more than 470 million people have signed a petition for canceling Brexit so far.
Problems Regarding the Brexit Deal
-Border Issue Between Northern Ireland and Ireland
The border issue is an important issue included in the withdrawal agreement. Northern Ireland is now part of the UK and is situated in the northern part of Ireland. Conflicts between nationalists who want to remain as part of the UK and coalitionists who want to be integrated with Ireland went through bloody conflicts accompanying physical fights and terrorist attacks for decades. This confrontation subsided after concluding the Belfast Agreement in 1998, allowing people to freely come-and-go between Northern Ireland and Ireland.

If a no-deal Brexit happens, however, the hard border between the two countries will be reintroduced. The UK and the EU have the same stance that the physical border should not be brought in, so they have agreed on a “backstop”, a safety net to ensure that there is no hard border between the UK and the EU, regardless of the outcome of future trade talks between the UK and the EU. If both sides do not reach agreement on trade until the year 2020, when the transition period ends, then the hard border would be recreated, ruining the unity of the UK. This would also create limitations on contracting trade agreements with other countries that the UK has not yet concluded trade agreements with.
-Low Public Support on the Brexit Deal
There are two reasons as to why citizens of the UK do not support the withdrawal agreement. Firstly, the contents of the Brexit deal are confusing. The withdrawal agreement claims to be a “soft Brexit”, whereas the declaration on future relations claims to be “hard Brexit”. Soft Brexit means remaining in the EU single market while maintaining status as a member nation in the European Economic Area (EEA), and only renouncing the right to participate in decision making regarding regulations on the single market. Hard Brexit, on the other hand, signifies that the UK leaves the EU right away and maintains their relationship under the regulations of the World Trade Organization (WTO), in the extreme case.

The “remain” side opposes the Brexit deal, saying it would trigger leaving the EU so as not to assure a soft Brexit. At the same time, the “leave” side is against it, citing that it would ultimately cause a soft Brexit, fading the meaning of withdrawal. Lastly, the public is divided in its opinions concerning the nation’s relationship with the EU, which is also the reason as to why the support to the Brexit deal is not strong.
Impacts of No-deal Brexit
-Impacts in the UK
➊ Economic Aspects
Multinational corporations in the UK are moving assets, companies, and employees from the UK to other EU member states or countries outside of the EU. In that case, the UK would suffer from mass dismissal, low economic growth, diminution in tax revenues, and such. The hard border would hinder active trade since 63% of the UK exports go to the EU, and more than 50% of the UK imports are from the EU. Also, in the case of a no-deal Brexit, the gross domestic product (GDP) rate would decrease by about 9.3%, according to the UK Exchequer’s analysis about the UK economy within about fifteen years after leaving the EU.
➋ Social Aspects
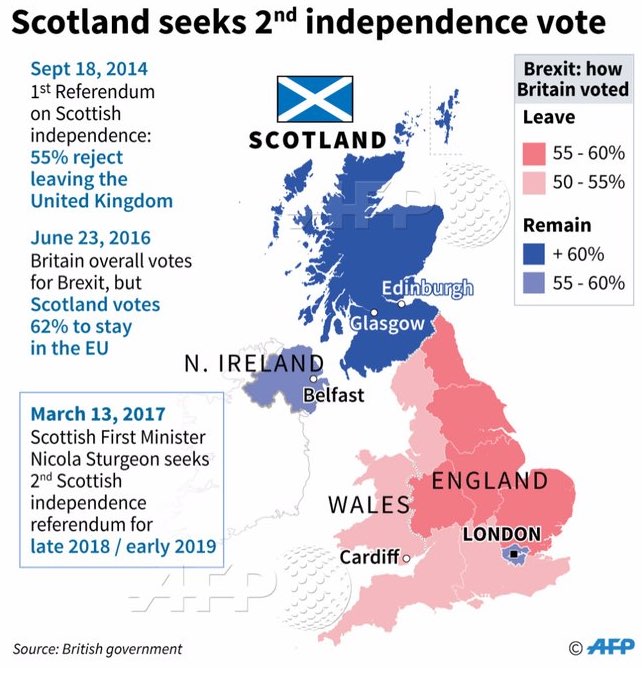
Different opinions on Brexit appear to have separated by generations and regions, which is problematic for the UK. The generations born after the UK joined the EU in 1973 mostly wants to stay in the EU, but many of the older generations want to leave the EU. In addition, Scotland and Northern Ireland predominantly agree on remaining, while Wales and England, except London, prevailingly insist on leaving, thus creating regional conflicts. Disputes with nationalism would re-emerge when the hard border is established between Northern Ireland and Ireland once again. Also, radical nationalists in Northern Ireland consider Brexit as an opportunity to reunite with Ireland, and the head of the Scottish government shows intentions to become independent of the UK and join the EU. Mrs. May is in a complicated situation because she will not be able to meet either of the demands of Northern Ireland and Scotland.
-Impacts in International Society
The United States (US) is reexamining its diplomatic policies in Europe because the UK is a country that represents its position in Europe. The US is also looking for another country that would replace the UK in Europe. On the other hand, Russia and China are looking forward to strengthening their relations with the UK. It is because the UK could make a breakthrough by being close to them in the case that relations become weaker with the US and part of Europe. In fact, the UK is expected to establish considerably cordial relations with China as the UK became the first Western country to participate in the founding of the Asia Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), even though the US dissuaded the UK not to. Lastly, export companies in South Korea could be affected by Brexit. South Korea has benefited from lower taxes and simple customs clearances thanks to a free trade agreement (FTA) with the EU, but a no-deal Brexit would generally raise tariff rates. Therefore, the government is trying to rework the contract on an individual FTA with the UK to minimize damages to companies.
Brexit or a no-deal Brexit is historically, economically, and politically a momentous issue. The negotiation period on the no-deal Brexit has been prolonged by Mrs. May. Now it is the time for the UK to endeavor to devise the best countermeasures and come to a consensus that the majority can agree upon
