An aging population is one of the most distinctive traits of modern society worldwide. As a result, increasing healthcare costs have become one of the main issues in many nations. This worldwide trend raised interest in biosimilar, or a cheap alternative for original drugs. In particular, Korea shows the fastest growth in its aging population among OECD countries, which indicates that the demand for biosimilar products should also be high. While some Korean biosimilar companies are just starting to gain attention in the global market, there are even expectations that this new industry might lead to a new “Korean wave.” The Sungkyun Times (SKT) takes a closer look at this promising medical industry and provides some possible ways to develop it as one of the core industries in Korea.
What is Biosimilar?
Definition
Biosimilar refers to the copy version of biological medicine (hence the name “bio” similar), manufactured after the patent period of the original product runs out. Biological medicine is a new form of medicine that uses biological ingredients such as proteins, genes, and cells from living organisms. Vaccines, insulin, and growth hormones are all good examples. Compared to original products, biosimilar products have the same efficacy but are made through different production processes. Unlike synthetic drugs, which are ordinary drugs made from chemical substances, copies of biological medicine cannot be 100 percent identical because slight differences can occur due to the deformation of the protein during the manufacturing process. Therefore, biosimilar medicine is not just an imitation of an original product, but a semi-new drug that uses the same materials as the original product but is made in its own unique way. Since biosimilar products are not exactly identical to the original product, they have to meet rigorous standards to prove that they have no difference from the original in terms of quality, safety, or efficacy. Biosimilar comparability exercises include three steps of clinical trials. The first and second trial both test stability and effectiveness of the biosimilar product. The final test is carried out on a much larger scale, with more than 500 participants.
The first official biosimilar product was “Omnitrope,” a derivative of a growth hormone. It was created by Sandoz Company and was approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in 2006. From then on, the biosimilar market has constantly been growing. Last year, its market scale reached $5 billion, which is more than seven times higher than the figure in 2012. Moreover, this market is expected to reach up to $20 billion by the year 2020.
Why Is It Gaining Popularity?
The biggest reason for the exponential growth of the biological medicine market is related to increasing demand for healthcare. Consequently, biosimilar is globally regarded as a new growth engine. In 2014, the world market scale of biological drugs was almost twice as large as the whole market scale of semiconductors, which is currently the main industry in Korea. In 2013, among the top ten medical products with the highest sales, seven of them were biological drugs. Because of the linkage effect, the larger the biological medicine market becomes, the greater the benefit that biosimilar receives. Furthermore, patents for early biological medicines, which emerged in the 1980s, are mostly set to expire between the year 2012 and 2020. This gives a new chance to pharmaceutical companies and facilitates active participation in the biosimilar market.
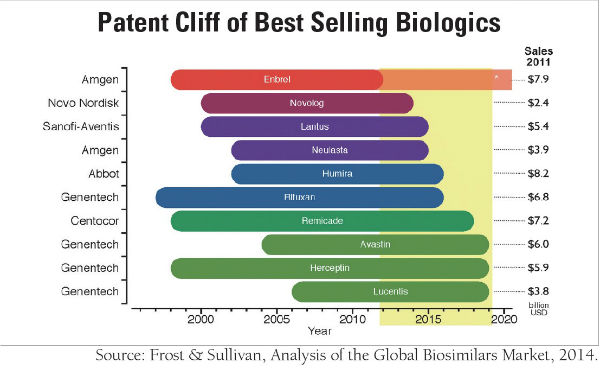
Lastly, the United States (US)’s changing view towards biosimilar products has also attracted numerous companies. While the US was reluctant to accept biosimilar products at first, it approved biosimilar products by enacting the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) in 2010 and is continuously trying to be more open to this new pharmaceutical option.
Biosimilar in Korea
Currently, Korean biosimilar companies are still in their fledging stages, having an eight percent market share of the entire market. Nevertheless, they are expected to have a growth spurt because Korean pharmaceutical companies are making immense investment in this industry.
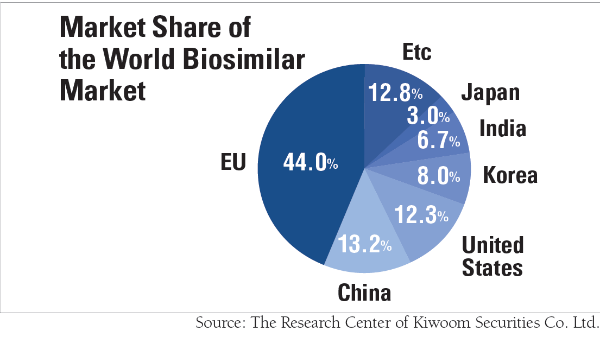
Celltrion is the most successful biosimilar company in Korea. Its main product, Rensima, has been approved by the Federal and Drug Administration (FDA), and it entered the US biosimilar market last August. This is meaningful in that Rensima is the second biosimilar product to be introduced in the US, which has the largest pharmaceutical market. Rensima’s debut to the world market seems to be successful, substituting about 20 to 30 percent of the biological products within a year.
Samsung, one of the biggest enterprises in Korea, has also jumped into the market, making a subsidiary company called Samsung Biologics. This strategic move stems from the judgment that only focusing on their current manufacturing-oriented business can no longer guarantee future growth. Gun-hee Lee, the Chairman of Samsung, has also said, “Businesses and products that are now representing Samsung will disappear in ten years.” Consequently, Samsung is intensively fostering biosimilar as a future strategic industry and has already started constructing large-scale factories in Songdo, Incheon. Once the construction is complete, Samsung will obtain the largest production capacity in the world market.
Merits and Concerns for Biosimilar Products
Advantages of Biosimilar Products
- Reasonable Prices
The most powerful and distinctive merit of biosimilar products is the low price. Usually, biological medicines cost much more than general drugs because they are monopolized by a single company and are produced through complex processes. On average, biological medicines are now about 22 times more expensive than general synthetic drugs. Furthermore, most biological medicines are prescribed for chronic diseases. Therefore, the burden on patients increases even more. Once biosimilar products are successfully introduced to the market, however, it is predicted to lower the price burden by 30 percent.
From the government’s perspective, this market is beneficial because it can save the government’s healthcare budget. IMS Health, a corporation specializing in statistical data analysis on healthcare, discovered that introducing biosimilar products will greatly benefit national finance. The introduction of biosimilar products will save funding in national health insurance of $56 billion to $110 billion over the next five years in both the US and European markets. From the patients’ point of view, this will largely improve the accessibility of costly biological medicines. For instance, Sandoz Company is now providing its main product, Zarxio, in a “Patient Support Kit.” This means that patients can self-administer the medicine at home. This easy access to biosimilar products is expected to especially benefit patients in the low-income class or in developing countries who cannot see doctors regularly.
- Increasing Opportunities for Small- and Medium-Sized Businesses
Traditionally, the pharmaceutical industry was only thought to be the exclusive property of select major companies. The biosimilar industry, however, has much lower entry standards for small-and medium-sized businesses. Developing a new biosimilar product has a lower risk because it takes only one-tenth of the cost and approximately half as much time compared to creating a new biological medicine. Despite these merits, the probability of success is almost ten times larger. Therefore, the influx of new entrants to the market will facilitate competition and will lead to the enhanced quality of overall medical products.
Barriers Faced by the Korean Biosimilar Industry
Negative Perception of the Public
Since biosimilar products are copies of original products, some people think the product has poor quality and is somewhat unreliable. Moreover, doctors are inclined toward a conservative prescription pattern, and this tendency does not easily change. Doctor’s unfavorable attitudes toward biosimilar products reinforce patients’ uncertainty. These factors all contribute to people’s loyalty to original products, making patients stick to the more expensive option. Therefore, the first mover gains a huge advantage, particularly in the pharmaceutical market.
Sabotage of Original Developers
Not surprisingly, developers of original drugs use various tactics to maintain their exclusive rights. They damage reputations of biosimilar products by creating anxiety in the market. Furthermore, they attempt to extend their patent’s expiration date, mostly by abusing loopholes in the current patent system. The “ever greening strategy” is one of the typical examples. This indicates a method of making only a minor change to a form or structure of the medicine in order to retain patent rights and keep any follow-up products away from the market. Last March, Samsung Biologics filed a suit against Abbvie, a multinational pharmaceutical company. Samsung claimed that it was unjust to extend the patent for Humira, the main product of Abbevie, from 2018 to 2022 because the new version shows no actual difference. Korean biosimilar companies should take some countermeasures to cope with such foul play.
Safety Issues
No matter how close biosimilar products may be to the original, the biosimilar differs in that it is not produced in an identical way to the original and might cause unexpected side effects. Considering that most original drugs have been prescribed for more than ten years, it is doubtful whether biosimilar products can be as stable as the original. Also, “indication extrapolation” is one of the issues surrounding the reliability of biosimilar products. This means that if a medication is approved to be effective for a certain disease, it is assumed that the medication has gone through full testing for all other similar conditions. In fact, biosimilar products can get a license only if they prove that the product is valid for a single disease. Even though biosimilar products go through some strict tests, the safety of biosimilar products should always be carefully monitored because clinical tests use limited time and few subjects.

Ways to Improve
Switching to Biobetter Products
In order to ensure long-term competiveness, Korean pharmaceutical companies should not just cling to biosimilar products. Instead, after gaining technical expertise from researching biosimilar products, they should develop biosimilar products into biobetter products. “Biobetter” is a medication that has been improved in terms of effectiveness or how often it should be administered. More simply stated, it can be explained as an upgraded version of the original. If companies manage to make a step forward in developing biobetter products, it would be possible for them to get their own patents and release their products regardless of patents for the original product.
Forming a Strategic Partnership
Many Korean biosimilar companies prefer to improve their technologies through their own research and development (R&D). Nevertheless, to obtain enough capital, technical skills, and large-scale capacity, it is a good option to cooperate with multinational corporations. Korean companies can consider potential mergers or acquisitions (M&A) or licensing contracts, which are contracts between two companies agreeing to share their knowledge. A good partner not only makes R&D easier, but also plays a significant role in local marketing.
Active Support from the Government
Given that the Korean biosimilar industry is at its beginning stage, biosimilar-friendly policies from the government can play a significant role in achieving global competitiveness. Germany is a good example that provides the most favorable environment for biosimilar products. Germany’s government has issued an initiative employing a minimum quota on a regional basis, requiring doctors to prescribe biosimilar products to a certain extent. It now also includes conducting an education session and sending a “Dear Doctors Letter” to straighten out misunderstandings over biosimilar products. This is meant to encourage doctors to prescribe biosimilar procucts. Consequently, Germany has grown to be Europe’s main source of biosimilar production.
As the famous saying goes, “Imitation is the mother of creation,” and copying is not always a negative thing. Biosimilar products can give an attractive opportunity to both pharmaceutical companies and patients who are desperately in need of affordable medicines. Hopefully, this new concept of medicine will successfully open a new chapter in the pharmaceutical industry.
